About the Archimedes Palimpsest
The Archimedes Palimpsest is a medieval parchment manuscript, now consisting of 174 parchment folios. While it contains no less than seven treatises by Archimedes, calling it the Archimedes Palimpsest is a little confusing. As it is now, the manuscript is a Byzantine prayerbook, written in Greek, and technically called a euchologion. This euchologion was completed by April 1229, and was probably made in Jerusalem.
The prayer book, or Euchologion, is itself of some interest, and further information on its contents can be discovered in this website. However, to make their prayer book, the scribes used parchment that had already been used for the writings of other books. The books they took parchment from were as follows.
The Book's Contents
Firstly, and most importantly, they used a book containing at least seven treatises by Archimedes. These treatises are The Equilibrium of Planes, Spiral Lines, The Measurement of the Circle, Sphere and Cylinder, On Floating Bodies, The Method of Mechanical Theorems, and the Stomachion. Of these treatises, the last three are of the greatest significance to our understanding of Archimedes. While the other treatises had survived through other manuscripts, there is no other surviving copy of On Floating Bodies in Greek – the language in which Archimedes wrote, and there is no version in any language of The Method of Mechanical Theorems and of the Stomachion. The Archimedes manuscript was used for the majority of the pages of the prayer book. The Archimedes manuscript was written in the second half of the tenth century, almost certainly in Constantinople.
Another book they used, we now know, contained works by the 4th century B.C. Attic Orator Hyperides. Prior to the discovery of the Hyperides text in the manuscript, this orator was only known from papyrus fragments and from quotations of his work by other authors. The Archimedes Palimpsest, however, contains 10 folios of Hyperides text.
Yet further books were used to make up the Palimpsest. Fourteen folios come from an otherwise unknown third century commentary on Aristotle's Categories, and 20 further folios come from four other books, two of which have yet to be identified.
How Was it Made?
How does one make one book out of seven? The answer is by palimpsesting them. The wordPalimpsest comes from the Greek Palimpsestos, meaning "scraped again". Medieval manuscripts were made of parchment, especially prepared and scraped animal skin. Unlike paper, parchment is sufficiently durable that you can take a knife to it, and scrape off the text, and over write it with a new text. In this case, seven books were taken apart, the text was scraped off the leaves, which were then stacked in a pile, ready for reuse.
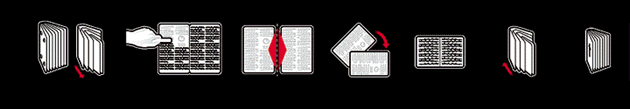
Medieval manuscripts are constructed like a whole series of newspaper. So each leaf has its conjoint, just as the front page of a news paper is attached to the back page. One should therefore imagine the leaves of the seven manuscripts as double-sheets, lying in a pile, without any text. To make the prayer book, these leaves were split down the middle, rotated ninety degrees and then refolded to make further double sheets that were half the size. The scribes then added their prayer book text, which is at ninety degrees to the now almost indecipherable erased writings.
What you see when you open the Archimedes palimpsest therefore, is not a mathematical text, nor even a piece of Greek oratory, but a prayer book. Only occasionally can one just discern, at right angles to the prayer book text, the erased writings that the current project is attempting to recover.
